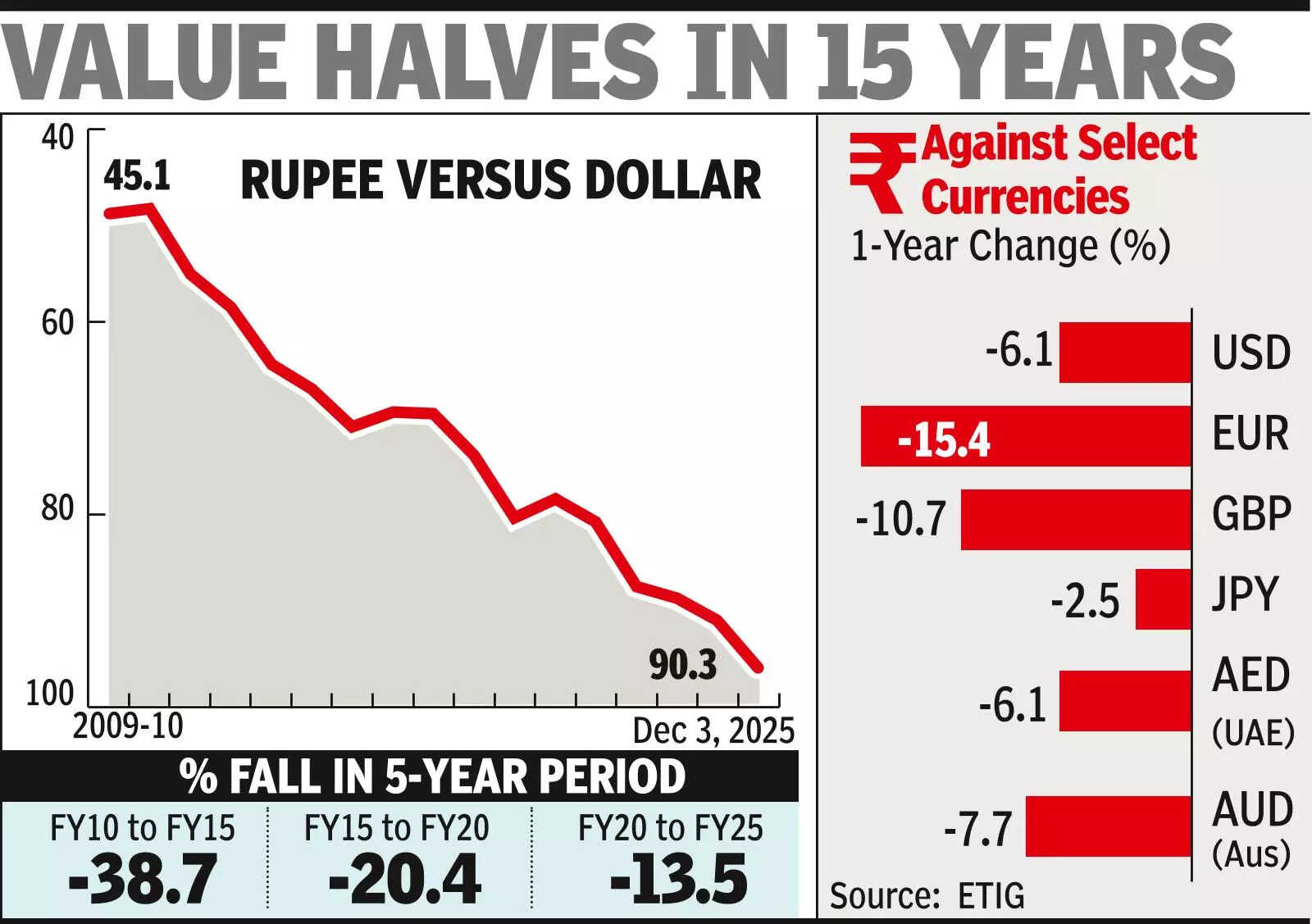
The Indian rupee plunged to a historic low of 90.29 against the US dollar, breaching the 90 mark for the first time. This sharp decline, attributed to US tariffs and significant foreign investor outflows, is now impacting the broader economy. While a weaker rupee makes imports costlier, it could benefit exporters and help manage the current account deficit.
Navigating the Choppy Waters: Understanding the Rupee’s Dip Below 90
The financial markets never sleep, and sometimes, they deliver a jolt that makes everyone sit up and take notice. Recently, we witnessed just that as the Indian Rupee dipped below the 90 mark against the US dollar for the first time ever. This isn’t just a number on a screen; it has real-world implications for businesses, consumers, and the Indian economy as a whole. So, what exactly is going on, and what does it mean for you?
Several factors have converged to create this downward pressure on the rupee. Imagine it like a tug-of-war, with various forces pulling the currency in different directions. One of the most significant influences is the prospect of escalating US tariffs. When the US imposes tariffs on imported goods, it can disrupt global trade flows and create uncertainty in the market. This uncertainty often leads investors to seek safer havens, typically the US dollar, thereby strengthening its value and weakening other currencies like the rupee.
Another key player in this drama is the flow of Foreign Institutional Investment (FII). FII represents investments made by foreign institutions in the Indian financial markets. When these institutions decide to pull their money out of India, it creates a supply of rupees in the market, further driving down its value. We’ve seen a considerable outflow of FII in recent weeks, adding to the downward pressure on the rupee. These fluctuations can often be attributed to changing global economic conditions and varying investor sentiment towards emerging markets like India.
The Impact of a Weaker Rupee: More Than Just Numbers
<img src="image-of-indian-currency-rupee.jpg" alt="A close-up image of Indian Rupee notes, symbolizing the impact of a weakened Indian Rupee on the economy.” width=”600″ height=”400″>
So, how does this all affect the average person and businesses operating in India? A weaker rupee makes imports more expensive. Think about the price of electronics, oil, and other goods that India relies on from overseas. As the rupee weakens, these goods become more costly, potentially leading to inflation. This can squeeze household budgets and put pressure on businesses that rely on imported raw materials.
However, a weaker rupee isn’t all doom and gloom. It can also benefit exporters. Indian companies selling goods and services abroad will find their products becoming more competitive in the global market. This is because their goods become relatively cheaper for foreign buyers. A boost in exports can, in turn, help improve India’s trade balance and provide a stimulus to the economy. For example, sectors like textiles, IT services, and pharmaceuticals could see increased demand.
Decoding the Currency Market
Understanding the currency market requires looking at a complex interplay of factors. It’s about understanding the intricacies of global finance and the influence of geopolitical events. Central banks play a crucial role in managing currency fluctuations. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), for instance, can intervene in the market by buying or selling rupees to stabilize its value. However, such interventions are often carefully calibrated, as aggressive interventions can have unintended consequences.
The broader economic landscape also plays a crucial role. Factors like India’s GDP growth rate, inflation levels, and fiscal deficit all influence investor confidence and, consequently, the value of the rupee. Strong economic fundamentals can attract foreign investment and support the currency, while economic instability can have the opposite effect. Consider reading our other article on [India’s economic outlook for next year](link-to-related-article) for a deeper dive.
Navigating the Future of the Rupee
Predicting the future of any currency is a notoriously difficult task. However, by closely monitoring key indicators such as US tariff policies, FII flows, and the overall health of the Indian economy, we can get a better sense of the potential trajectory of the rupee. Businesses need to be prepared for volatility and develop strategies to mitigate the risks associated with currency fluctuations. This might involve hedging currency risks or diversifying their export markets.
For the average consumer, understanding the broader economic context can help in making informed financial decisions. While the value of the rupee is beyond individual control, being aware of the factors that influence it can empower you to make better choices about spending, saving, and investment.
Ultimately, the recent dip in the rupee’s value serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of the global economy and the importance of staying informed about the forces that shape our financial landscape. While short-term fluctuations are inevitable, a focus on long-term economic stability and sound financial policies will be crucial in ensuring the strength and resilience of the Indian Rupee in the years to come.