Following the Air India Flight 171 crash, the FAA and Boeing have privately affirmed the safety of fuel switch locks on Boeing aircraft. India’s AAIB preliminary report questioned if the fuel switches were accidentally activated, leading to engine failure. The FAA issued a notification stating the fuel control switch design doesn’t warrant an Airworthiness Directive.
Air India’s Close Call: Unraveling the 2006 Engine Shutdown
Remember that heart-stopping moment when you’re on a plane and something just…doesn’t sound right? For passengers on an Air India flight back in 2006, that unnerving feeling became a stark reality. A newly released report sheds light on the intricate chain of events that led to an engine shutting down mid-flight, offering valuable insights into aviation safety and the critical role of both human factors and mechanical safeguards.
The incident, though years in the past, continues to resonate within the aviation community as a crucial learning opportunity. The US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and Boeing have both weighed in on the investigation’s findings, highlighting the significance of a particular fuel switch lock system. But what exactly happened, and why is it still relevant today?
The flight in question was cruising smoothly until a sudden engine failure threw everything into chaos. Initial reports suggested a possible malfunction, but the investigation delved deeper, revealing a complex interplay of factors. It turns out that the way the fuel was being managed was a primary contributor.
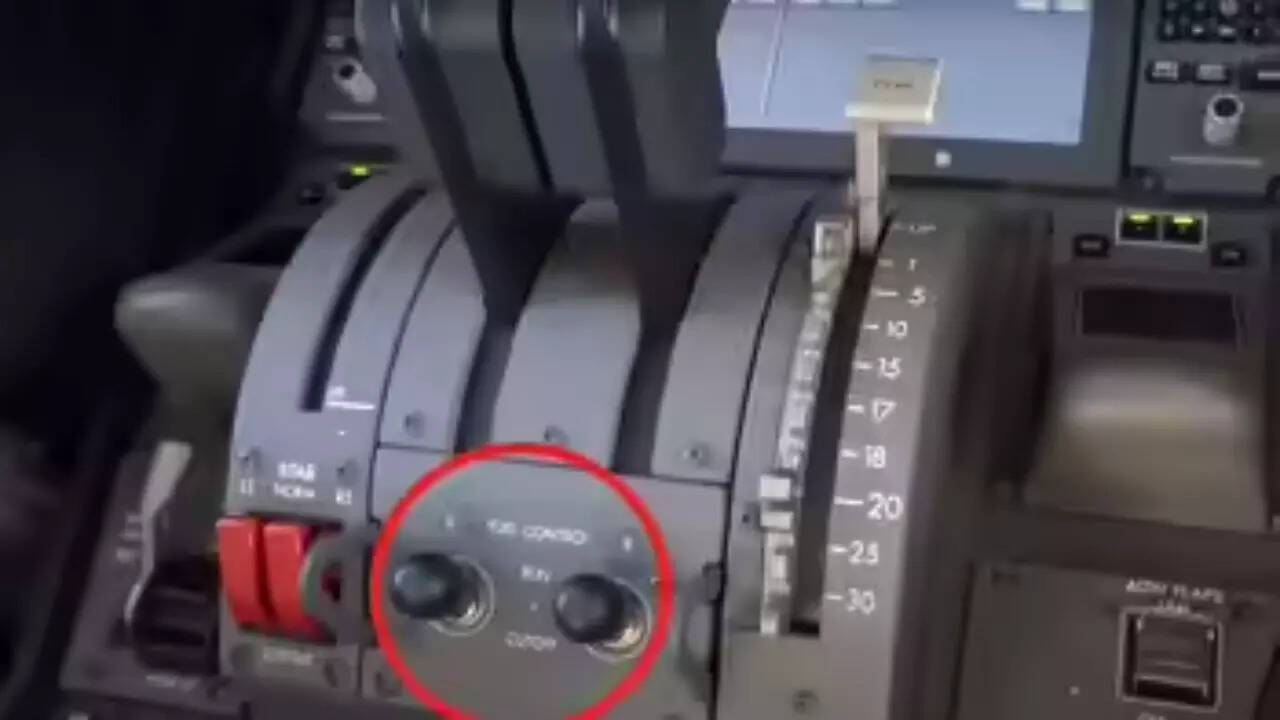
Specifically, the report examined the fuel switch lock system. This is a critical component designed to prevent pilots from inadvertently cutting off fuel to an engine during flight. The system is intended to act as a safeguard, ensuring that such a drastic measure is only taken when absolutely necessary – like in the event of a fire or catastrophic engine failure.

The probe revealed questions surrounding the engine cutoff. In this instance, investigators explored whether the safety mechanisms in place were sufficient to prevent an accidental shutdown, or whether other elements such as pilot training or system design could have played a role.
The key takeaway is that while mechanical failures can happen, human factors often contribute to incidents. Understanding how pilots interact with complex systems, and identifying potential areas for error, is paramount. Boeing’s involvement in the investigation underscores the manufacturer’s commitment to continuous improvement and the enhancement of safety features across their aircraft.
What makes this case particularly interesting is the focus on preventative measures. It’s not just about understanding what went wrong, but about implementing changes that will prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. This could involve modifications to the fuel switch lock system itself, enhanced pilot training protocols, or improvements to cockpit warning systems.
The incident also brings attention to the often-unseen complexities of modern aircraft operation. Passengers rightly place their trust in the pilots and crew, but behind the scenes, a vast network of engineers, technicians, and regulatory bodies work tirelessly to ensure the safety of every flight. The Air India event highlights the critical importance of their collaborative efforts.
We’re continually learning from past incidents. The FAA’s collaboration with Boeing on this investigation demonstrates a proactive approach to aviation safety. This commitment extends beyond individual airlines or aircraft types, fostering a culture of continuous improvement across the entire industry. This dedication to improvement benefits us all.
Ultimately, the story of Air India’s near miss serves as a valuable reminder of the dedication and vigilance required to maintain the highest standards of aviation safety. By carefully analyzing past incidents, implementing necessary changes, and fostering a culture of continuous learning, the aviation industry can continue to make air travel the safest form of transportation.
The incident underscored the need for a more failsafe fuel switch lock and better training. What safeguards should be in place to prevent similar human error?